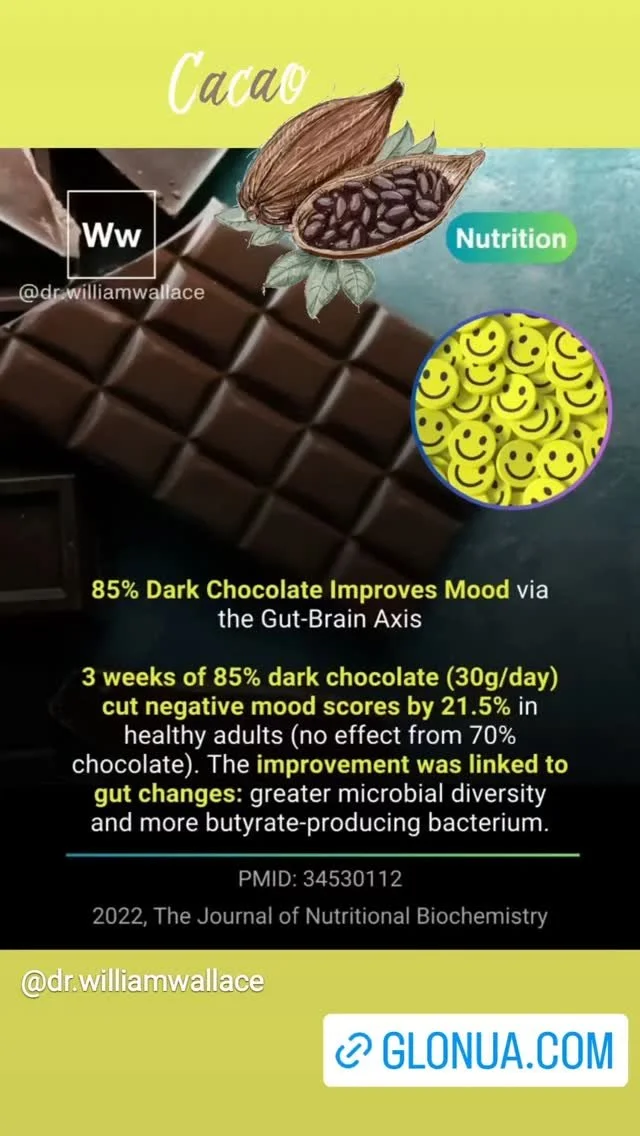
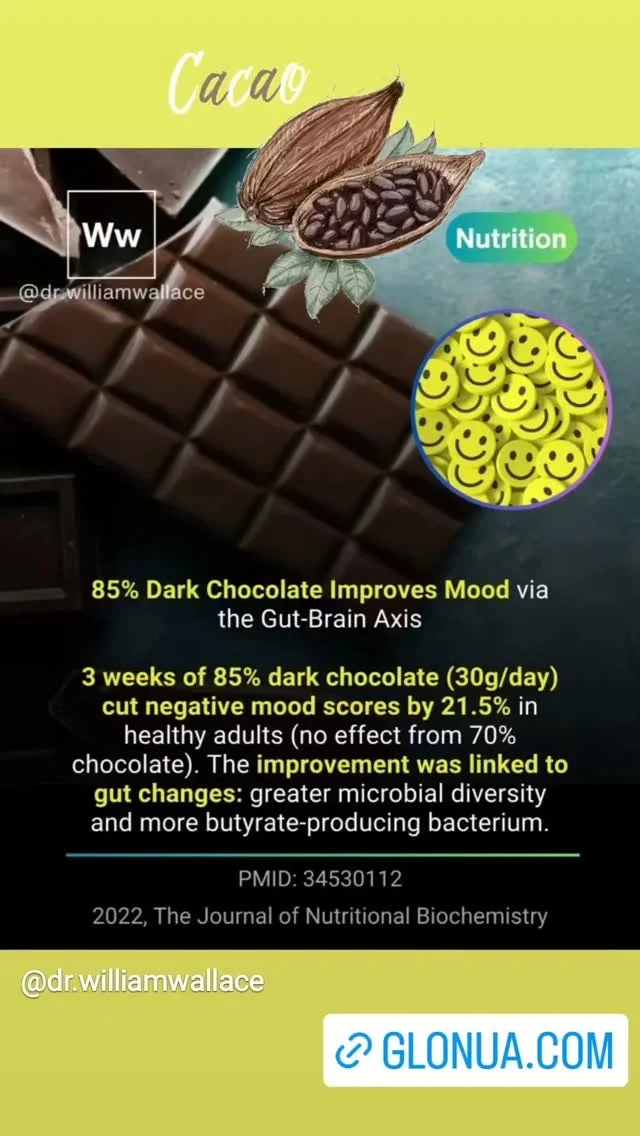
Vitamin D a fat-soluble Sunshine Vitamin.
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that is obtained from sun exposure, food, and dietary supplements . Vitamin D promotes calcium absorption from the gut where it is transported to both the liver and the kidneys to become biologically active and ready for use in the body. Vitamin D is primarily used by the skeletal system in maintaining bone stability and allowing for muscle relaxation. Aside from its skeletal targets, the main destination of Vitamin D is fat cells.
Adipose tissue is commonly known as body fat. Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin, meaning it requires being attached to a fat molecule in order to be absorbed, transported, and stored. Although it was previously thought of as just storage cells sitting around, adipose tissue has since been classified as an endocrine organ that plays a role in whole-body energy metabolism and inflammation.
There is an association between vitamin D deficiency and obesity. Literature suggests that vitamin D is sequestered in fat cells in overweight and obese individuals, preventing it from reaching its targets of the bone and muscles. With weight loss, vitamin D is released from fat storage cells into the bloodstream, temporarily increasing vitamin D levels.
In mice fed a high-fat diet, those supplemented with vitamin D gained less weight than those who did not consume vitamin D. It is proposed that cells with vitamin D favor the use of lipids as an energy source, thus reducing the storage of lipids as fat and reducing adipose cell formation.
Recently, Vitamin D has been in the news regarding its potentially immunoprotective role in numerous Infectious Diseases such as Flu, colds & COVID-19. Clinical trials found that patients with vitamin D levels above normal limits had a reduced number of flu, cough days and less olfactory sensory loss with infection. It is proposed that vitamin D heightens specific immune markers and enhances the degradation of the virus through acidification of the infected cells, leading to a faster clearance of the virus and expedited recovery.
The connection between adipose tissue and vitamin D is a complex network that scientists are continuing to map out.